CONMAN
Data-driven CONtrol and MANifold interpolation
Data-driven CONtrol and MANifold interpolation
Pulsed jEt actuatoRs for SEparation control of tUrbulent flowS
Published in Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2014
Publisher: Cambridge University Press
Recommended citation: Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Jean-Christophe Robinet, Stefania Cherubini, Emmanuel Leriche, "Investigation of the roughness-induced transition: global stability analyses and direct numerical simulations." Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2014. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-fluid-mechanics/article/abs/investigation-of-the-roughnessinduced-transition-global-stability-analyses-and-direct-numerical-simulations/0D62A95BD1FD2D2C664A8EDABCFAFC46
Published in Eur. J. Phys., 2016
Publisher: IOP Publishing
Recommended citation: James Fannon, Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Prashant Valluri, Iain Bethune, Lennon Náraigh, "High-performance computational fluid dynamics: a custom-code approach." Eur. J. Phys., 2016. https://doi.org/10.1088/0143-0807/37/4/045001
Published in European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids, 2016
Recommended citation: A. Ducoin, J. Loiseau, J. Robinet, "Numerical investigation of the interaction between laminar to turbulent transition and the wake of an airfoil." European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids, 2016. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0997754615302685
Published in Fluid Dyn. Res., 2016
Publisher: IOP Publishing
Recommended citation: J.-Ch Loiseau, J.-Ch Robinet, E. Leriche, "Intermittency and transition to chaos in the cubical lid-driven cavity flow." Fluid Dyn. Res., 2016. https://doi.org/10.1088/0169-5983/48/6/061421
Published in Journal of Fluid Science and Technology, 2017
Use Google Scholar for full citation
Recommended citation: S. Miyauchi, T. Hayase, A. Banaei, J.-Ch. loiseau, L. Brandt, F. Lundell, "Two-dimensional numerical simulation of the behavior of a circular capsule subject to an inclined centrifugal force near a plate in a fluid." Journal of Fluid Science and Technology, 2017.
Published in Phys. Rev. Fluids, 2017
Publisher: American Physical Society
Recommended citation: Outi Tammisola, Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Luca Brandt, "Effect of viscosity ratio on the self-sustained instabilities in planar immiscible jets." Phys. Rev. Fluids, 2017. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.2.033903
Published in European Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2017
Publisher: Taylor \& Francis _eprint: https://doi.org/10.1080/17797179.2017.1294828
Recommended citation: Arash Alizad, Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Iman Lashgari, Luca Brandt, "Numerical simulations of elastic capsules with nucleus in shear flow." European Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1080/17797179.2017.1294828
Published in Journal of Computational Physics, 2018
Recommended citation: Zhouyang Ge, Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Outi Tammisola, Luca Brandt, "An efficient mass-preserving interface-correction level set/ghost fluid method for droplet suspensions under depletion forces." Journal of Computational Physics, 2018. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021999117308136
Published in Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2018
Publisher: Cambridge University Press
Recommended citation: M. Bucci, D. Puckert, C. Andriano, J.-Ch Loiseau, S. Cherubini, J.-Ch Robinet, U. Rist, "Roughness-induced transition by quasi-resonance of a varicose global mode." Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2018. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-fluid-mechanics/article/abs/roughnessinduced-transition-by-quasiresonance-of-a-varicose-global-mode/6301B3D53B94E007A087033CCA972DE0
Published in Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2018
Publisher: Cambridge University Press
Recommended citation: Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Steven Brunton, "Constrained sparse Galerkin regression." Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2018. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-fluid-mechanics/article/abs/constrained-sparse-galerkin-regression/0E18A4A55FF5AC1401D236C0E4D1CAAE
Published in J. Fluid Mech., 2018
Recommended citation: Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Bernd Noack, Steven Brunton, "Sparse reduced-order modelling: sensor-based dynamics to full-state estimation." J. Fluid Mech., 2018. https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/identifier/S0022112018001477/type/journal_article
Published in Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2018
Publisher: Cambridge University Press
Recommended citation: F. Picella, J.-Ch Loiseau, F. Lusseyran, J.-Ch Robinet, S. Cherubini, L. Pastur, "Successive bifurcations in a fully three-dimensional open cavity flow." Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2018. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-fluid-mechanics/article/abs/successive-bifurcations-in-a-fully-threedimensional-open-cavity-flow/7E7D87FF453E91FF728563567F278CCB
Published in European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids, 2019
Recommended citation: Souvik Ghosh, Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Wim-Paul Breugem, Luca Brandt, "Modal and non-modal linear stability of Poiseuille flow through a channel with a porous substrate." European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids, 2019. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0997754618301833
Published in Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019
Publisher: Cambridge University Press
Recommended citation: Y. Bengana, J.-Ch Loiseau, J.-Ch Robinet, L. Tuckerman, "Bifurcation analysis and frequency prediction in shear-driven cavity flow." Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-fluid-mechanics/article/abs/bifurcation-analysis-and-frequency-prediction-in-sheardriven-cavity-flow/2309FAE82EDBFA35AFF0D5A389F55323
Published in Journal of Open Source Software, 2020
Publisher: The Open Journal
Recommended citation: Brian Silva, Kathleen Champion, Markus Quade, Jean-Christophe Loiseau, J. Kutz, Steven Brunton, "PySINDy: A Python package for the sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems from data." Journal of Open Source Software, 2020. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.02104
Published in Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn., 2020
Recommended citation: Jean-Christophe Loiseau, "Data-driven modeling of the chaotic thermal convection in an annular thermosyphon." Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn., 2020. https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00162-020-00536-w
Published in Phys. Rev. Fluids, 2021
Publisher: American Physical Society
Recommended citation: M. Bucci, S. Cherubini, J.-Ch. Loiseau, J.-Ch. Robinet, "Influence of freestream turbulence on the flow over a wall roughness." Phys. Rev. Fluids, 2021. https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.6.063903
Published in Proc. R. Soc. A., 2021
Recommended citation: J. Callaham, J.-C. Loiseau, G. Rigas, S. Brunton, "Nonlinear stochastic modelling with Langevin regression." Proc. R. Soc. A., 2021. https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rspa.2021.0092
Published in AIAA Journal, 2022
Publisher: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics _eprint: https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J061001
Recommended citation: Andrea Sansica, Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Masashi Kanamori, Atsushi Hashimoto, Jean-Christophe Robinet, "System Identification of Two-Dimensional Transonic Buffet." AIAA Journal, 2022. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.J061001
Published in Sci. Adv., 2022
Recommended citation: Jared Callaham, Georgios Rigas, Jean-Christophe Loiseau, Steven Brunton, "An empirical mean-field model of symmetry-breaking in a turbulent wake." Sci. Adv., 2022. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abm4786
Published in J. Fluid Mech., 2022
arXiv:2106.02409 [physics]
Recommended citation: Jared Callaham, Steven Brunton, Jean-Christophe Loiseau, "On the role of nonlinear correlations in reduced-order modeling." J. Fluid Mech., 2022. http://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02409
An open-source toolbox for large-scale hydrodynamic stability analyses for the spectral element solver Nek5000.
A package for the sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems from data.
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Master Program, Arts et Métiers, 2019
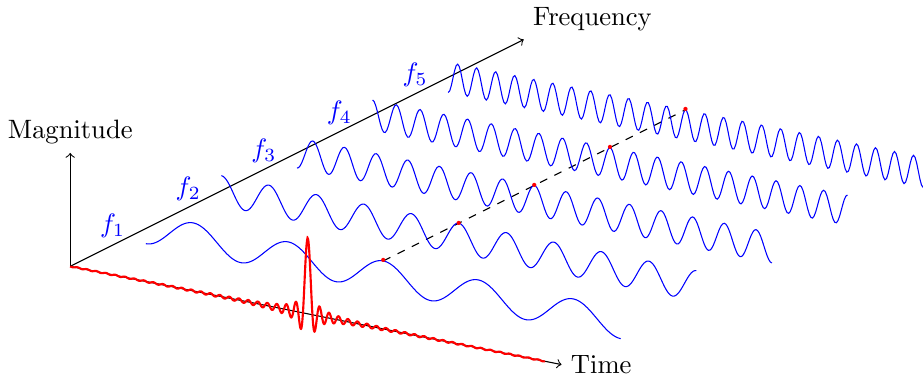 This short course is part of the international master program Factory of the future proposed by Arts et Métiers Institute of Technology. Note that students enrolling in this program may come from very different backgrounds. As such, the aim of this course is to teach them the basics of Fourier analysis and signal processing. One or two small numerical projects in
This short course is part of the international master program Factory of the future proposed by Arts et Métiers Institute of Technology. Note that students enrolling in this program may come from very different backgrounds. As such, the aim of this course is to teach them the basics of Fourier analysis and signal processing. One or two small numerical projects in python or octave are also proposed.
Master Program, Arts & Métiers, 2019
This course is part of the international master program Factory of the future proposed by Arts et Métiers Institute of Technology. Students enrolling in this program may come from very different backgrounds. As such, the aim of this course is to teach them the basic tools from linear algebra (linear systems of equations, vector spaces, eigenvalues and eigenvectors) and discrete-time MIMO linear systems they may need for other courses in this program. One or two small numerical projects in python or octave are also proposed.
Master Program, Arts et Métiers - UPMC, 2019
 This course is part of the master program M2 Aérodynamique et Aéroacoustique proposed jointly by Université Pierre et Marie Curie and Arts et Métiers Institute of Technology. Its aim is to give students an overview of the typical behaviours dynamical systems can exhibit (i.e. fixed points, periodic orbits, quasi-periodic dynamics and temporal chaos) and how to study them (e.g. fixed point computation, linear stability, bifurcation and normal form theory, Takens embedding theorem, etc). Most of the course consists in sessions of two-hour long lectures with a few exercises. A small numerical project in
This course is part of the master program M2 Aérodynamique et Aéroacoustique proposed jointly by Université Pierre et Marie Curie and Arts et Métiers Institute of Technology. Its aim is to give students an overview of the typical behaviours dynamical systems can exhibit (i.e. fixed points, periodic orbits, quasi-periodic dynamics and temporal chaos) and how to study them (e.g. fixed point computation, linear stability, bifurcation and normal form theory, Takens embedding theorem, etc). Most of the course consists in sessions of two-hour long lectures with a few exercises. A small numerical project in python or julia on realistic systems from fluid dynamics or classical mechanics is also proposed.
Master Program, Arts et Métiers, 2019
This short course is part of the international master program Factory of the future proposed by Arts et Métiers Institute of Technology. This course is not mandatory. Hence, having only a handful of students enrolling each year, it consists in a series of hands-on tutorials rather than dedicated lectures. The aim is that, by the end of the course, students are able to implement in python a simple two-dimensional Navier-Stokes solver based on pseudospectral methods for two-dimensional turbulence in a doubly periodic domain.
Ingénieur 2000, Arts et Métiers, 2020
This short course is part of the program FIP (no idea what it stands for) proposed by Arts et Métiers Institute of Technology. Its aim is to introduce students to scientific computing with python. Because the audience consists mostly of engineering students spending half of their time in industry, the idea is to have some “fun” time rather than a lengthy course about scientific computing. To do so, the course consists in a series of small projects oriented toward pratical applications. In the process, they will learn the basics of data manipulation with numpy, visualization with matplotlib and optimization with scipy. Another proper course on scientific computing using matlab is also proposed in this program wherein students will learn the basics of numerical differentiation and data analysis.